⛰️ DEM Hillshade#
Generate hillshade map from Digital Elevation Model (DEM).
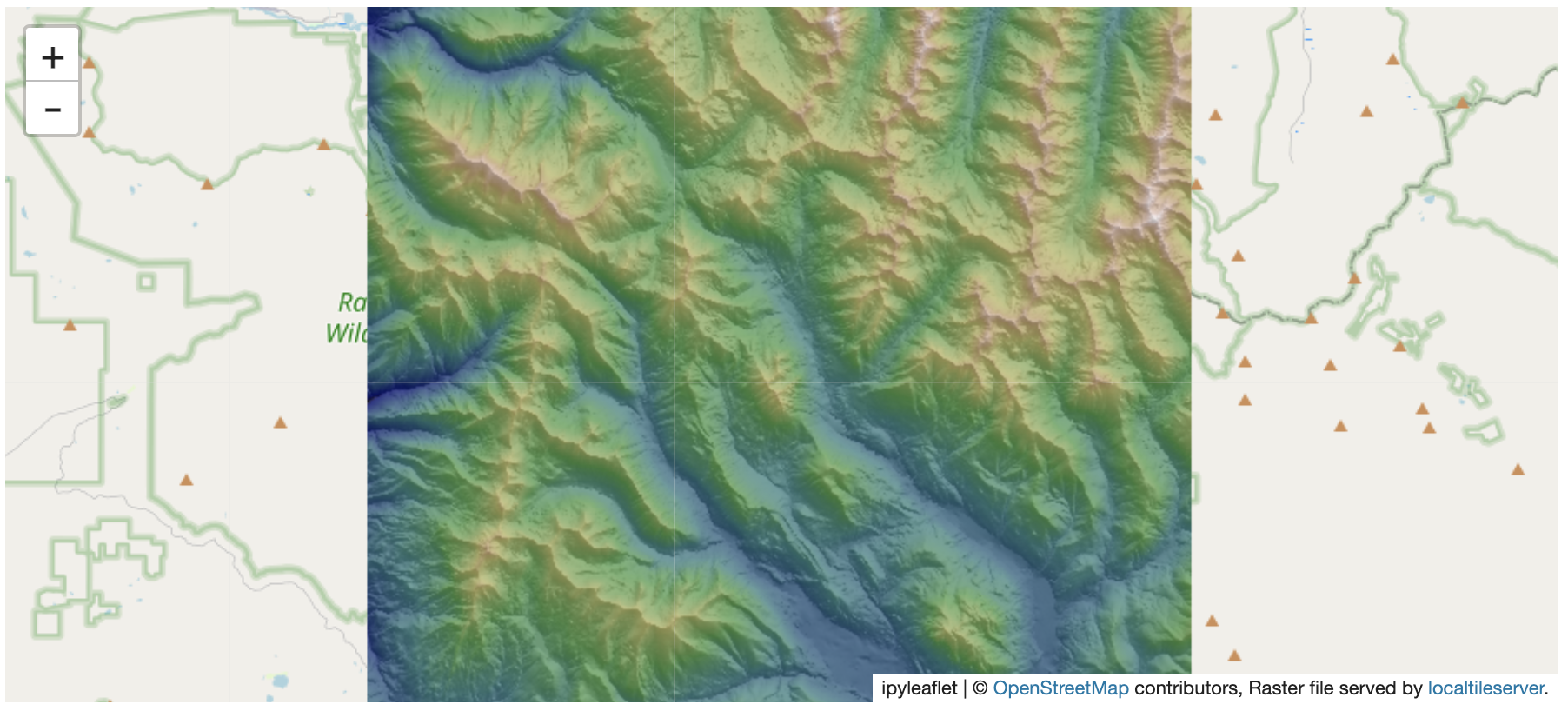
A hillshade is a 3D representation of a surface where the darker and lighter colors represent the shadows and highlights that you would visually expect to see in a terrain model. Hillshades are often used as an underlay in a map, to make the data appear more 3-Dimensional.
Note
This example was adopted from EarthPy
from localtileserver import TileClient, get_leaflet_tile_layer
from localtileserver import examples, helpers
from ipyleaflet import Map, SplitMapControl
import rasterio
# Example DEM dataset
client = examples.get_co_elevation()
tdem = get_leaflet_tile_layer(client, colormap='gist_earth', nodata=0)
m = client.get_leaflet_map()
m.add(tdem)
m
Read the DEM data as a NumPy array using rasterio:
dem = client.dataset.read()[0, :, :]
dem.shape
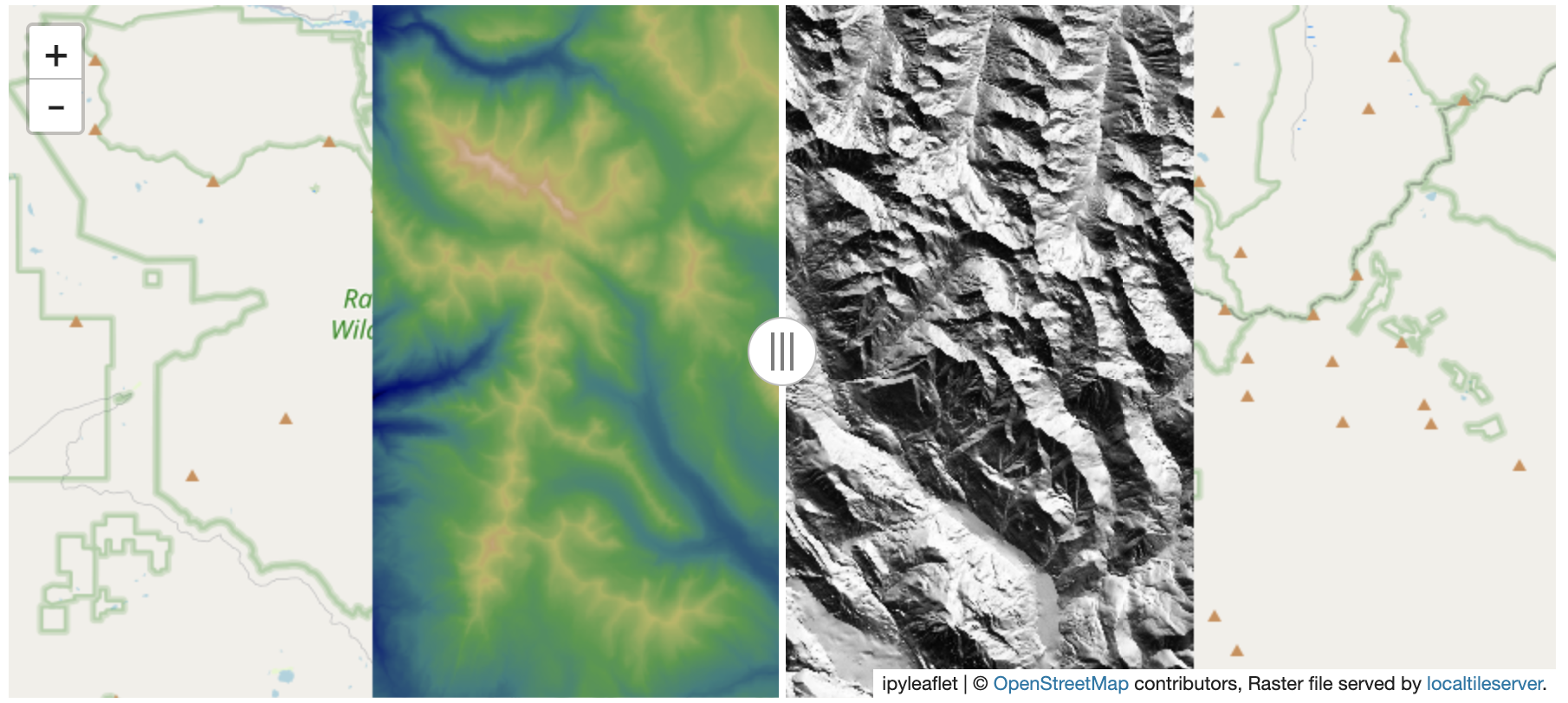
Compute the hillshade of the DEM using the localtileserver.helpers.hillshade()
function (adopted from EarthPy).
help(helpers.hillshade)
# Compute hillshade
hs_arr = helpers.hillshade(dem)
# Save hillshade arrays as new raster and open with rasterio
hs = rasterio.open(helpers.save_new_raster(client, hs_arr))
# Make an ipyleaflet tile layer of the hillshade
hst = get_leaflet_tile_layer(hs, nodata=0)
m = client.get_leaflet_map()
control = SplitMapControl(left_layer=tdem, right_layer=hst)
m.add_control(control)
m

We can also overlay the hillshade on the original DEM so that it gives it a 3D effect:
m = client.get_leaflet_map()
m.add(tdem)
m.add(get_leaflet_tile_layer(hs, opacity=0.5, nodata=0))
m